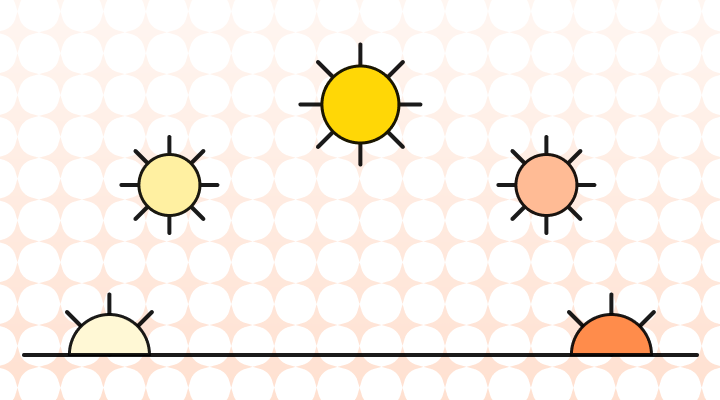
⏰ What time of day is it in the photo below? ⏰
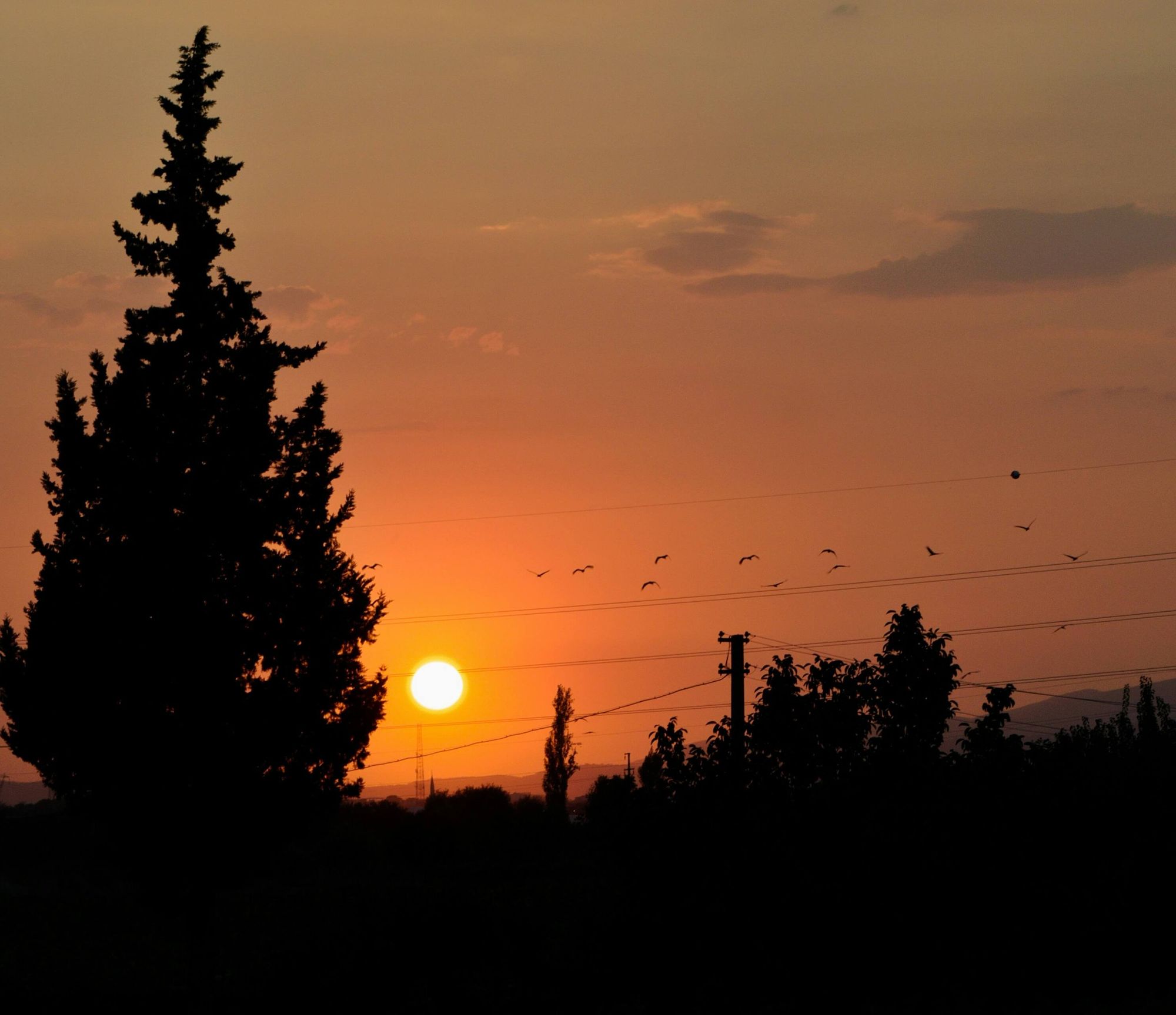

Would you be able to answer this question in a few seconds, and would you be 100% sure of your answer? If not, this blog post will help you master the vocabulary for the various times throughout the day.

We have defined the ten times of the day, provided tips on their usage, and explained the various expressions associated with time, so that you can incorporate these time indicators with certainty.
Table of Content
- What does "day" mean?
- Ten times of the day
- Grammar rules
- Example sentences
- The etymology of the ten different times
- Common phrases
- Idioms
- Conclusion
What does "day" mean?
Before going into detail about the different terminologies of time, let's start off with the word "day." "Day" has three definitions.
- "Day" can refer to the range of time between sunrise and sunset.
- "Day" can also refer to the 24-hour period.
- "Day" can also refer to the calendar day.
Examples:
- The beautiful sunrise marked the beginning of a new day filled with endless possibilities.
- Every day presents us with new challenges and opportunities for growth.
- Despite the rain, today turned out to be a great day spent with friends and family.
- Seize the day and make the most out of every moment.
- After a long day at work, I look forward to unwinding and relaxing in the evening.
Ten times of the day
- Dawn: The time of day when light first appears, before sunrise.
- Sunrise: The time when the sun rises at the start of the day.
- Morning: The period from midnight to noon.
- Noon/Midday: The middle of the day, 12:00 PM.
- Afternoon: The period after midday until evening.
- Evening: The period from the end of the afternoon until 12:00 PM.
- Sunset: The time when the sun sets, marking the beginning of the night.
- Dusk: The time of day just after sunset, when light is fading.
- Night: The period from sunset to sunrise when it is dark outside.
- Midnight: The middle of the night; 12:00 AM.
Below is an infographic of the different times throughout the day. Please feel free to use this however you choose.
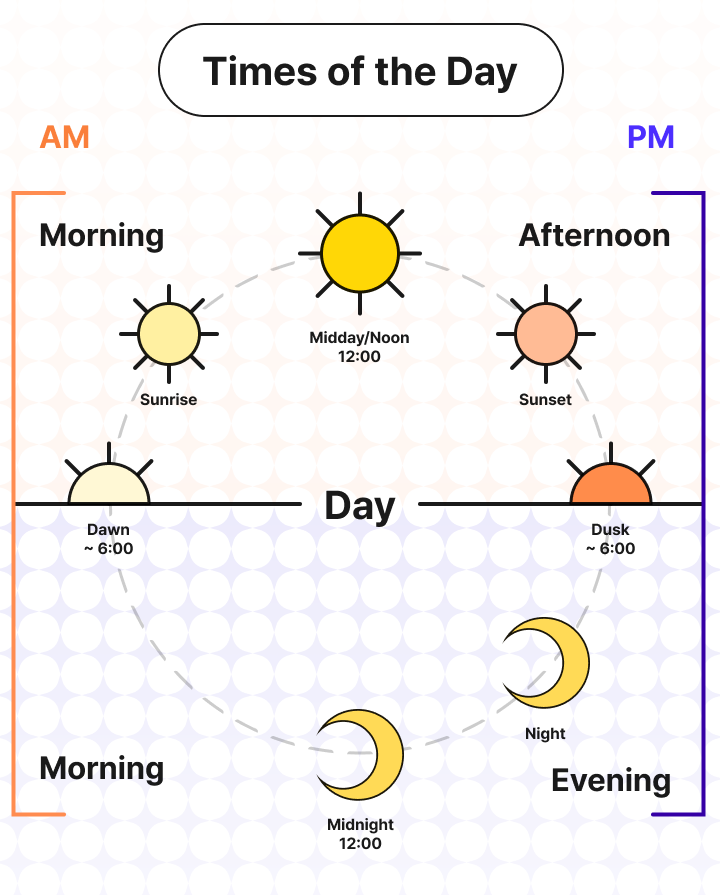
Daylight: Daylight refers to the duration of time when sunlight is apparent.
Nighttime: Nighttime refers to the duration between sunset and sunrise. It is usually describing the time when there is no light.

Grammar rules
Parts of speech
The ten terms are usually either an adjective or a noun.
Time adverbs
We can also use more specific phrases to describe times within these larger categories. For example, we might say "early morning" or "late afternoon."
Prepositions of time
We use at and in for phrases associated with time.
At
"At" denotes a specific time. In the twelve expressions, the six below use "at" before them.
e.g. dawn, sunrise, noon/midday, sunset, dusk, midnight
In
"In" indicates a wider range of time. In the twelve expressions, the three below use "in the" before them.
e.g. morning, afternoon, evening
Night is an exception
Although "night" covers a more general range of time, the preposition "at" precedes "night." This is because "at night" has become an idiomatic expression. "In the night" is not grammatically wrong, but it is used less frequently and is typically used in poetic or literary contexts.
Other prepositions: during, before and after
"During" is used to indicate a period of time in which an event or action takes place.
- For example, during the sunset, we were drinking wine.
"Before" indicates a point in time that is earlier than the time mentioned.
- For example, we decided to go to bed before midnight.
"After" is a point in time that comes after the event or action that took place.
- For example, after noon, we went for a hike because the weather was cooler.

Example sentences
Dawn
- At dawn, the fishermen set out on their boats, eager to catch the day's fresh haul.
"Dawn" is a noun, and the preposition "at" is before the noun.
Sunrise
- We woke up early to catch the breathtaking sunrise at the beach.
In the sentence above, "sunrise" is used as a noun and an object, with the adjective "breathtaking" describing its beauty.
- At sunrise, the birds began their melodic chorus, filling the tranquil morning air with their song.
"Sunrise" is a noun here, and as it indicated a specific point in time, we used "at" before it.
Morning
- In the morning, I enjoy sipping a cup of coffee while reading the newspaper.
The "morning" in this sentence is a noun, and it has "in the" preceding it.
- The morning air was crisp and invigorating as we embarked on our hike.
In this sentence, "morning" is an adjective. "Morning" describes the "air" on the hike.
Noon/Midday
- At noon, the sun was directly overhead, casting few shadows.
"Noon" in this sentence is a noun that describes the time of the sun's movement. "At" is used before it.
- The midday sun was scorching.
"Midday" in this phrase is an adjectivethat describes the sun.
Afternoon
- In the afternoon, I usually take a short break to go for a walk.
"Afternoon" is a noun in this sentence and is used with "in" as a prepositional phrase before it.
Check out our video about using the correct preposition for "afternoon."
Evening
- We enjoyed a leisurely dinner in the evening, watching the sunset from our balcony.
"Evening" is a noun in this sentence and denotes the time when the family took their dinner. "In" is used before "evening."
- The evening dress is beautiful.
The word "evening" is used as an adjective here to describe "dress."
Sunset
- The colors of the sky were ablaze with hues of red and gold during the breathtaking sunset.
"Sunset" is a noun, and for this noun, the preposition used is "during." Although "at" is used before sunset, the preposition "during" can be used before sunset if it is referring to a duration.
Dusk
- We took a stroll through the forest at dusk, listening to the sounds of nature.
The preposition "at" is used before "dusk." Dusk is also used as a noun.
Night
- The city came alive at night, with neon lights illuminating the streets.
"At" is used before "night," which is a noun in this sentence.
Midnight
- At midnight, the streets were deserted, bathed in the soft glow of moonlight.
"Midnight" functions as a noun in this sentence. "At" is used before "midnight."

The etymology of the ten different times
- Dawn: Derived from the Old English word "dagung" meaning "daybreak."
- Sunrise: Literally, the rising or ascent of the sun. The term "sunrise" originates from the combination of "sun" and "rise."
- Morning: Originates from the Middle English "morn."
- Noon/Midday: "Noon" comes from the Old English "non," which likely originated from the Latin "Nona Hora," meaning "ninth hour" (counting from sunrise). "Midday" is self-explanatory, indicating the middle of the day.
- Afternoon: Literally, the time after noon. It combines "after" with "noon."
- Evening: Evening comes from the Old English word "ǣfnung," that referred to the time of day between afternoon and nightfall. This term eventually became "evening" as we know it today.
- Sunset: Literally, the setting or descent of the sun. The term "sunset" combines the words "sun" and "set."
- Dusk: Derived from the Old English "dox," meaning "darkness."
- Night: The word "night" has a rich etymology that traces back through several languages and historical periods. It is derived from the Old English term "niht."
- Midnight: Literally, the middle of the night. The term "midnight" combines "mid" with "night."
Common phrases
Dawn
- At the crack of dawn
- Dawn chorus
Sunrise
- Watch the sunrise
Morning
- Good morning
- Morning person
Noon/Midday
- Lunchtime
Afternoon
- Good afternoon
- Afternoon slump
- Afternoon sun
Evening
- Good evening
- Evening stroll
- Evening news
Sunset
- Watch the sunset
- Sunset glow
Dusk
- Twilight
- Dusk settles
- Dusk chorus
Night
- Good night
- Nightfall
- Night sky
Midnight
- Midnight snack
- Burning the midnight oil
- Midnight rendezvous
Idioms
Make hay while the sun shines: Take advantage of favorable conditions or opportunities while they last.
- Example: Let's make hay while the sun shines and finish this project before the deadline approaches.
The early bird catches the worm: Those who act promptly or get up early are often the most successful.
- Example: The early bird catches the worm, so I woke up at dawn to be the first in line for the limited edition release.
Every cloud has a silver lining: Even in difficult or dark times, there is usually a positive aspect or outcome to be found.
- Example: Despite the setback, she remained optimistic, believing that every cloud has a silver lining, and saw it as an opportunity for personal growth.
Tomorrow is a new day: Each day brings new opportunities and a chance for a fresh start.
- Example: After a challenging day, she reminded herself that tomorrow is a new day, full of fresh opportunities and possibilities.
The sun never sets on the British Empire: This proverb originated during the height of the British Empire, emphasizing its vast territorial holdings around the world.
- Example: The saying "The sun never sets on the British Empire" once reflected the vast extent of British colonial territories across the globe.
A day without laughter is a day wasted: It's important to find joy and humor in each day.
- Example: Embracing the philosophy that "a day without laughter is a day wasted," she made it a point to find humor in even the most mundane moments.
Carpe diem (Seize the day): Make the most of the present moment; don't waste time.
- Example: "Carpe diem," he whispered to himself as he made the decision to take the leap and pursue his lifelong dream without hesitation.
Rome wasn't built in a day: Complex or significant achievements take time and effort to accomplish.
- Example: She reminded herself that progress takes time, repeating the old adage "Rome wasn't built in a day" as she patiently worked towards her goals.
Conclusion
To answer the question asked at the beginning of the post, the timing of the photo is "sunset." Referencing time is something we do on a daily basis, but have we taken a step back to wonder whether we are naming the time of day correctly? Hopefully, this blog post will provide more confidence to tackle the times of the day and confidently provide an answer when someone asks, "What time of day is it?" next.

References:
Times of Day in English