Research methodology refers to the systematic process and techniques used by researchers to conduct research and gather data.
The term refers to the specific way of conducting research and collecting information, including individual tools, techniques, and even behaviors. It is a critical aspect of the research process and plays a crucial role in ensuring the validity, reliability, and credibility of research findings. The research methodology ultimately aims to help answer research questions or test hypotheses in an organized and credible fashion. The what, where, and how of the research is decided upon and the research can also incorporate multiple different methods which may include:
- Experiments
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Ethnography
- Longitudinal studies
- Participant observation
- Data mining
Research methodology encompasses various components and steps, including:
- Research Design: Researchers decide on the overall approach and structure of their study. This includes choosing between qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods research, determining the research scope, and selecting the appropriate research methods.
- Data Collection: Researchers gather relevant data or information to address their research questions. This can involve methods such as surveys, interviews, experiments, observations, archival research, or data mining, depending on the research design.
- Sampling: In cases where it is not feasible to study an entire population, researchers select a representative sample from the population. Sampling methods should be carefully chosen to avoid bias and ensure the generalizability of findings.
- Data Analysis: After collecting data, researchers employ various analytical techniques and statistical methods to analyze and interpret the data. The choice of analysis methods depends on the research objectives and the type of data collected.
- Research Ethics: Researchers must adhere to ethical principles and guidelines when conducting research, ensuring the rights, privacy, and confidentiality of participants. Ethical considerations are a fundamental aspect of research methodology.
- Instrumentation: Researchers design or select appropriate tools, instruments, and questionnaires to collect data accurately and reliably. They must validate and pilot these instruments when necessary.
- Data Presentation: Research findings are typically presented in a clear and organized manner, often using tables, graphs, charts, and textual explanations.
- Peer Review: Research methodology includes the practice of subjecting research studies to peer review, where experts in the field evaluate the study's design, methods, and findings for quality and accuracy.
- Replicability: A critical aspect of research methodology is ensuring that other researchers can replicate the study's methods and obtain similar results. This promotes transparency and confidence in research findings.
- Continuous Improvement: Researchers may refine their methodology as they progress, learning from the research process and making adjustments to enhance the quality of their work.
Effective research methodology is essential for producing reliable and valid research results, and it varies depending on the specific field of study, research objectives, and available resources. Researchers must carefully plan and execute their methodology to ensure the rigor and credibility of their research findings.
The use of the term "research methodology" over time
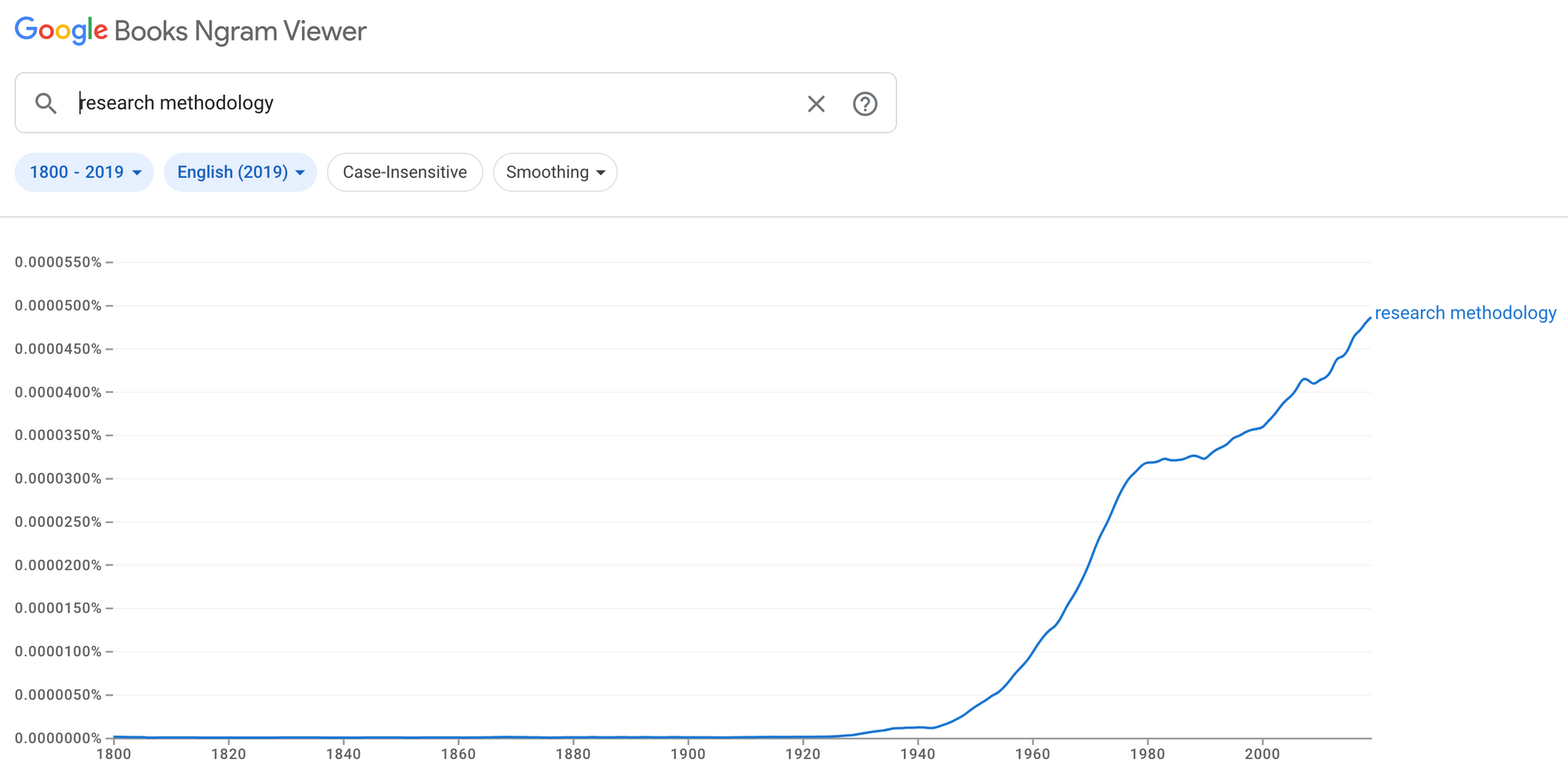
The use of the term "research methodology" has experienced an upward trend since the 20th century, most likely continuing to rise to this day. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the earliest known use of "research methodology" was in Science Magazine in 1920, so the term is relatively new when considering the whole history of the English language.
Example sentences
- The success of the research project depended on choosing the appropriate research methodology.
- The professor emphasized the importance of a well-defined research methodology in our thesis proposals.
- The research methodology section of the paper outlined the data collection techniques used in the study.
- The research team followed a qualitative research methodology to explore participants' experiences.
- Before conducting the survey, the researchers carefully designed the research methodology to ensure valid results.
- The research methodology included both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods for a comprehensive analysis.
- Peer reviewers praised the research methodology section for its clarity and rigor.
- The research methodology employed a mixed-methods approach, combining surveys and interviews.
- The research methodology chapter of the dissertation explained the steps taken to address potential biases.
- The research methodology adopted in this study was consistent with industry best practices.
Want to sound like a native speaker?
Engram’s AI-powered grammar checker makes your English sound like a native speaker’s, suggesting natural English expressions on top of fixing grammar, spelling, punctuation, word order, and vocabulary.

Reference:



https://research.com/research/how-to-write-research-methodology















