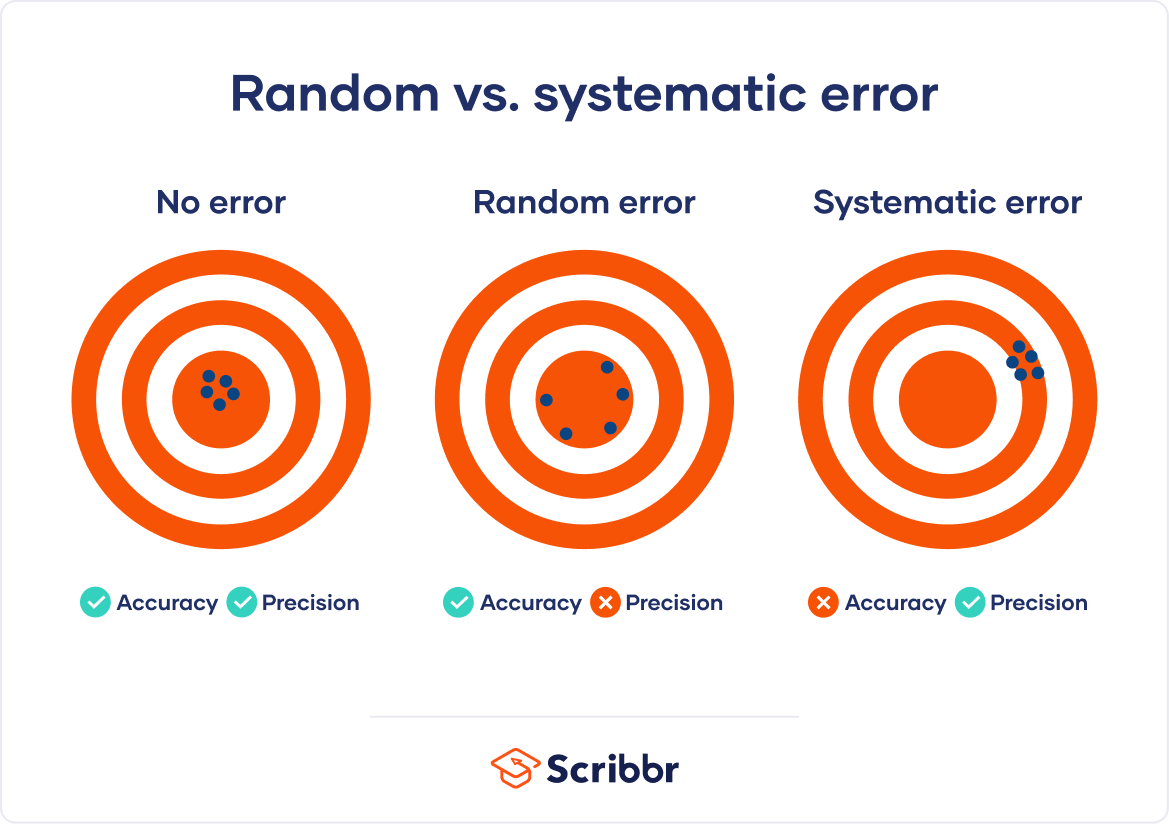
Random error is unpredictable and irregular variation in measurements, while systematic error is consistent and repeatable deviation from the true value in measurements.
In the realm of both English language and scientific measurement, two seemingly contrasting terms— "random" and "systematic" errors—play pivotal roles. Understanding the nuances between these words is crucial not only for effective communication but also for maintaining accuracy in various fields, from mathematics and science to everyday discourse.

In this blog post, we'll delve into the meanings, differences, and usages of "random" and "systematic" errors, shedding light on why these concepts are vital in both language and precision-driven domains.
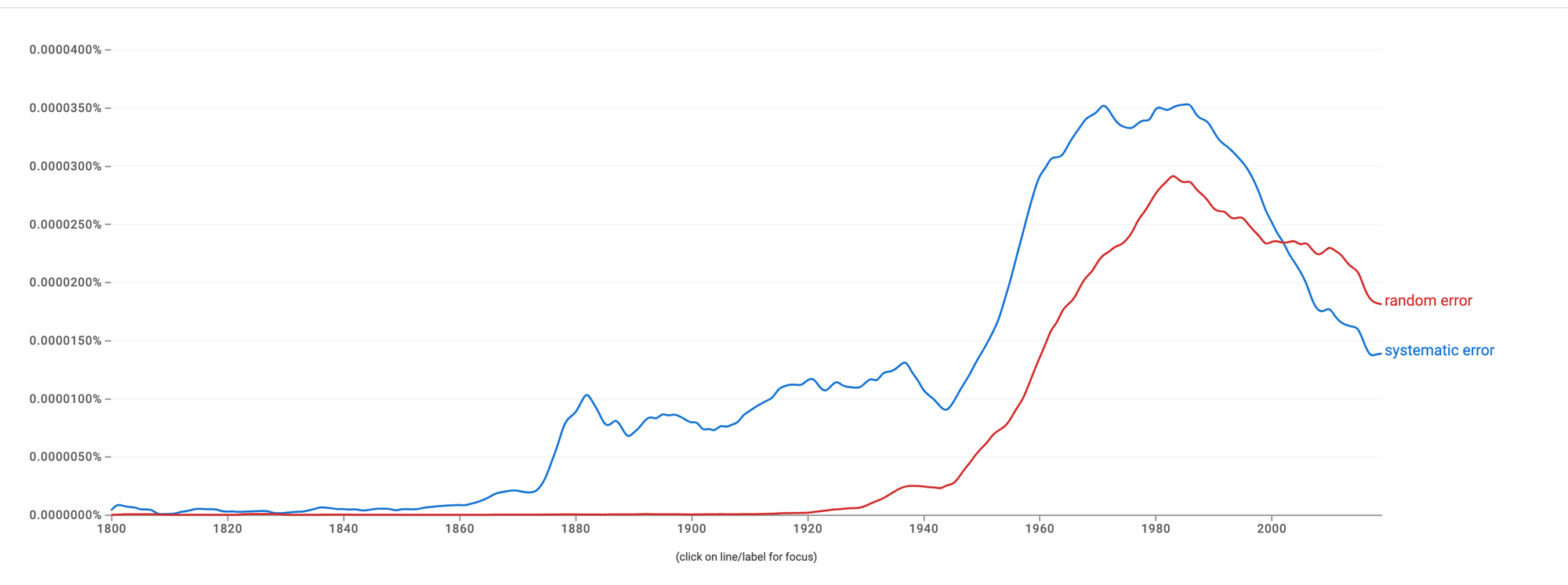
In the graph below, you can see the variance in which both words have been used over two centuries.
What is a random error?
- "Random error" refers to unpredictable or irregular variations that occur during measurements or observations.
- It is characterized by deviations from the true value that are not consistent or systematic.
- Random errors can be caused by various factors, including environmental conditions, instrumentation limitations, and human factors.
Example scenario
In a series of weight measurements, if the scale occasionally gives slightly different readings due to vibrations in the room, these variations are considered random errors.
What is a systematic error?
- "Systematic error," on the other hand, is a consistent and repeatable deviation from the true value in measurements.
- It arises from flaws or biases in the measurement process, equipment, or methodology.
- Unlike random errors, systematic errors are not random or unpredictable; they affect measurements in a consistent and often skewed manner.
Example scenario
If a thermometer consistently reads temperatures 2 degrees Celsius higher than the actual temperature due to a calibration issue, this is a systematic error.
Common Idioms/Phrases:
- "Systematic approach": This phrase refers to a methodical and organized way of addressing a problem or undertaking a task, typically with attention to detail and order.
Synonyms:
When discussing these concepts, you can also consider using these synonyms for variety:
Random Error:
- Unpredictable variation
- Irregular deviation
- Chance fluctuation
Systematic Error:
- Consistent deviation
- Bias
- Methodical flaw
Which is worse: random or systematic errors worse?
Whether systematic or random errors are "worse" depends on the context and the specific goals of a measurement or analysis.
Systematic Errors: These errors can be considered more problematic in some cases because they consistently skew measurements in one direction. Systematic errors are often caused by flaws in measurement instruments, calibration issues, or biases in the measurement process. Since they are consistent, systematic errors can lead to results that are consistently incorrect, making it challenging to identify and correct them. However, because they are consistent, they may be easier to detect and correct once identified.
Random Errors: Random errors, on the other hand, introduce variability and uncertainty into measurements. While they can make measurements less precise, they do not consistently push measurements in one direction. In some cases, random errors can be reduced through repeated measurements and statistical analysis. They can be considered "worse" when high precision is required, such as in scientific experiments or engineering, as they can affect the ability to draw precise conclusions.
In summary, the severity of systematic or random errors depends on the context and the goals of the measurement. In many cases, both types of errors need to be addressed and minimized to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Practice questions
- The random/systematic error in the experiment resulted from fluctuations in temperature that affected the measurements.
- The scientist discovered a random/systematic error in the data collection process that consistently skewed the results.
Answer Key:
- Random
- Systematic
Understanding the distinctions between "random" and "systematic" errors not only sharpens your language skills but also ensures precision in various scientific and analytical endeavors. So whether you're discussing measurement accuracy or practicing kindness, you'll navigate these concepts with confidence and clarity.
Want to sound like a native speaker?
Engram’s AI-powered grammar checker makes your English sound like a native speaker’s, suggesting natural English expressions on top of fixing grammar, spelling, punctuation, word order, and vocabulary.

Reference: