"Maintainability" refers to the ease with which a system, product, or asset can be maintained, repaired, or serviced over its lifecycle.
Maintainability involves the ability to optimize the maintenance process while minimizing downtime and costs. It is a key consideration in the design and development of various systems and products, including technology, machinery, infrastructure, and software. Maintainability aims to ensure that a system remains in good working condition and can be efficiently and cost-effectively serviced when needed.
Example: Machinery in a factory
For instance, imagine a piece of machinery in a factory. Suppose it is a complex machine that is difficult to fix and restore to its default condition. A highly skilled engineer would be required to come in and fix it if it is malfunctioning, and they would have to spend a relatively long time to fix it. However, the machine rarely malfunctions because it was extremely carefully created in the first place and only requires occasional checkups. The maintainability of the machinery would depend on these different factors, and the factory would have calculated this before purchasing or creating the machinery.

Key aspects of maintainability include:
- Accessibility: The ease with which maintenance personnel can access components and parts that require servicing or replacement. In our example above, the machinery is extremely complex, so the components are likely to be difficult to replace or restore.
- Modularity: Designing a system with interchangeable and easily replaceable modules or components, simplifying maintenance. The complicated machinery in our example above would likely have custom-made parts that are not easy to replace.
- Documentation: Providing comprehensive and clear documentation, including maintenance manuals, schematics, and repair instructions. The creators of the complex machine in the example above would have likely written a clear manual and repair instructions.
- Simplicity: Designing systems and products with straightforward and standardized components and processes, reducing complexity. In our example above, the machinery was not, in fact, simple. It is an intricate machine that requires high maintenance if broken.
- Predictive Maintenance: Implementing systems and sensors to monitor the condition of assets, allowing for proactive maintenance before failures occur. The complex machinery in our example above likely has predictive maintenance that helps it not malfunction often, making the need for repairs rare and sparse.
- Spare Parts Availability: Ensuring the availability of necessary spare parts and minimizing lead times for replacements.
- Training: Providing training to maintenance personnel to ensure they have the skills and knowledge to perform maintenance tasks effectively.
Synonyms for "maintainability"
Although no single word has the exact same meaning and nuances as "maintainability," the following are words most similar to the term:
- Serviceability
- Repairability
- Accessibility
- Durability
- Reliability
- Manageability
These terms are often used interchangeably in different contexts, but they may emphasize slightly different aspects of the overall concept of maintaining systems and products.
The use of "maintainability" throughout the years
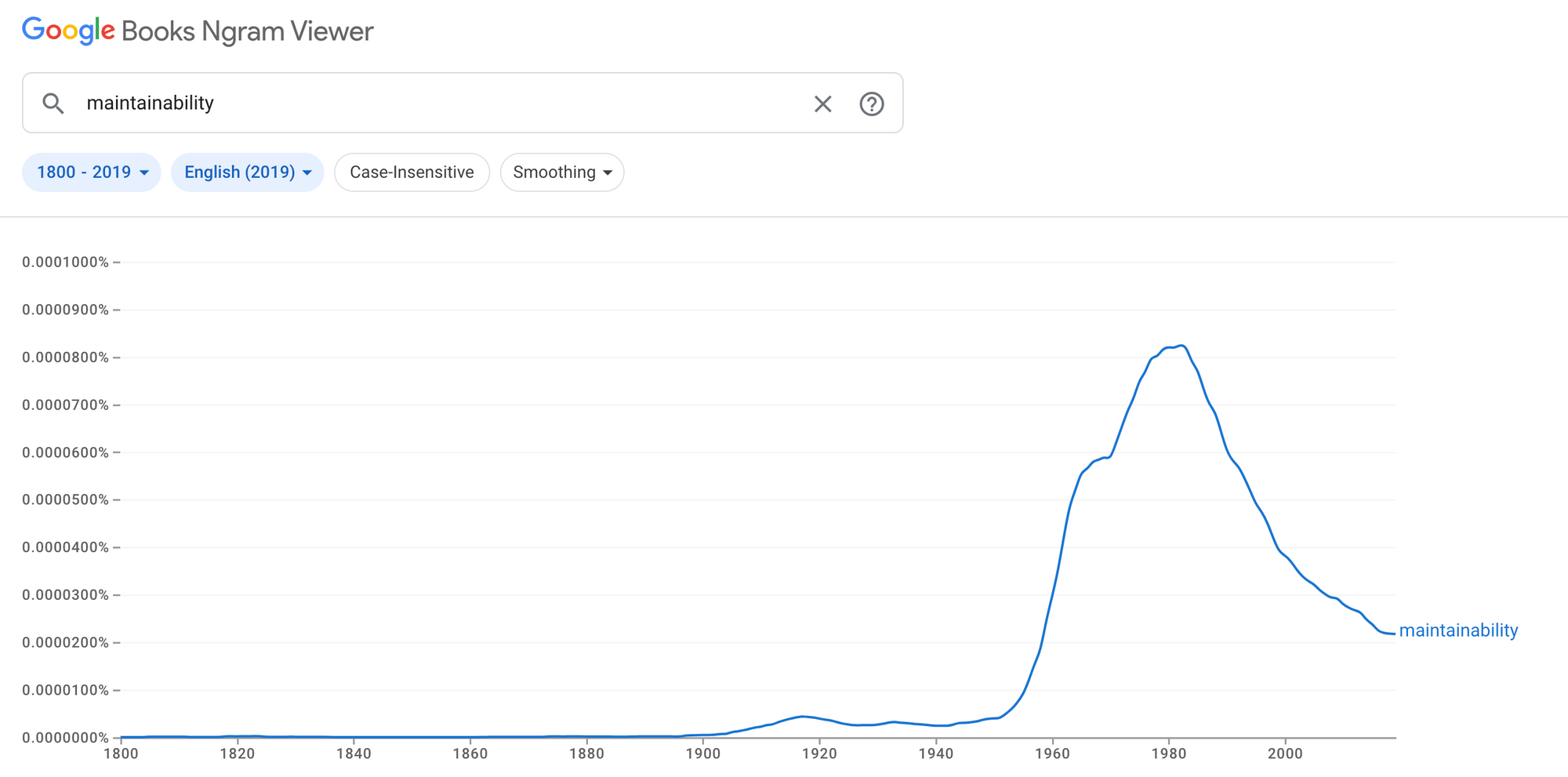
As shown in the image above, the word "maintainability" experienced a peak in the 1980s around the time when home computers were becoming popular.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the earliest known evidence of the noun "maintainability" is from 1856 in the Dublin Evening Mail, one of Ireland's longest-running evening newspapers.
Example sentences
- The maintainability of the new software system proved to be a significant improvement over the previous version.
- Engineers prioritize the maintainability of complex machinery to reduce downtime and repair costs.
- Regular maintenance checks are essential for ensuring the long-term maintainability of industrial equipment.
- The architect designed the building with a focus on both aesthetics and maintainability, making it easier to perform repairs when needed.
- The automotive industry places a high premium on the maintainability of vehicles to enhance customer satisfaction.
- One of the key challenges in aircraft design is achieving the right balance between performance and maintainability.
- The IT team conducted a review to assess the maintainability of the network infrastructure and identified areas for improvement.
- The software developer implemented coding practices that improve the maintainability of the codebase.
- Homeowners often overlook the importance of regular maintenance for the long-term maintainability of their properties.
- In the field of infrastructure development, considering the maintainability of public structures is crucial for their sustainability.
Want to sound like a native speaker?
Engram’s AI-powered grammar checker makes your English sound like a native speaker’s, suggesting natural English expressions on top of fixing grammar, spelling, punctuation, word order, and vocabulary.

Reference:

https://www.getmaintainx.com/learning-center/what-is-maintainability/
https://limblecmms.com/maintenance-definitions/what-is-maintainability/
https://www.lawinsider.com/dictionary/maintainability